Abstract

Despite excellent outcomes for CLL patients treated with covalent BTK inhibitors, many patients ultimately acquire resistance due to cysteine 481 mutations in BTK. Non-covalent BTK inhibitors, such as pirtobrutinib, are active against C481 mutations but susceptible to other BTK mutations (including L528W, V416L, M437R, and T474I mutations), most of which also confer resistance to covalent BTK inhibitors.
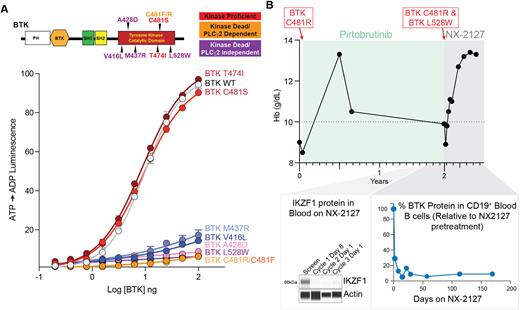
Although BTK resistance mutations impede drug binding, here we make the surprising observation that drug resistance substitutions at L528W, M437R, and V416L disable BTK's enzymatic activity yet still enable B cell receptor (BCR) signaling, suggesting a nonenzymatic, or scaffolding, activity. In vitro kinase assays of full-length wild-type BTK and 8 distinct BTK mutant proteins revealed that BTK C481R, C481F, L528W, and V416L have near complete absence of kinase activity (Figure). While BTK C481R/F mutations were recently shown to be kinase dead, these mutant proteins are still dependent on phosphorylation of PLCγ2 Y1217, the downstream substrate of activated BTK. By contrast, BTK L528W, M437R, and V416L mutations promote BCR signaling in a distinct manner independent of PLCγ2 Y1217 phosphorylation. Consistent with these results, expression of L528W, M437R, and V416L mutations in BTK knockout DT40 cells failed to result in BTK Y223 autophosphorylation or phosphorylation of PLCγ2.
Despite the above findings, BTK kinase dead mutants augmented signaling downstream of BCR following IgM stimulation with intact activation of AKT, ERK, and hyperactivated calcium release. Single cell transcriptomic analyses of BTK inhibitor resistant CLL cells revealed upregulation of BCR transcriptional signatures, NFκB, and IKZF2/3 target genes.
To understand how kinase dead BTK mutants enhanced BCR signaling, we performed global phosphoproteomics, kinobead assays, and BTK immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry studies in BTK-dependent human B cell lymphoma cells expressing WT or kinase-dead BTK L528W. Collectively these studies revealed a unique physical interaction of BTK L528W with LYN and HCK, as well as activation of these kinases and their phosphorylated substrates compared with WT BTK. This suggests that PLCγ2-independent BTK kinase dead mutants bypass BTK/PLCγ2 to activate BCR signaling via a scaffolding function of mutant BTK.
To address the lack of enzymatic activity in these mutant BTK proteins, we explored means to eliminate, rather than enzymatically inhibit, BTK. We generated NX-2127, a potent, heterobifunctional, orally bioavailable degrader molecule which brings both BTK as well as IKZF proteins into close proximity with the E3 ligase adapter protein cereblon, triggering their ubiquitylation and subsequent degradation. Importantly, NX-2127 induced complex formation of CRBN and WT BTK as well as BTK C481S and T474I mutants as shown via a FRET-based biochemical assay. In fact, NX-2127 bound WT and the gatekeeper BTK T474I mutant with similar binding affinity. Consistent with this, NX-2127 promoted dose-dependent degradation of WT BTK and each recurrent drug resistant mutant (BTK C481S, L528W, V416L, T474I, and M437R). In addition, degradation of WT as well as BTK mutants blocked IgM-dependent stimulation of BCR signaling.
The above findings motivated a first-in-human phase 1 trial of NX-2127 in relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies (NCT04830137). One exemplary CLL patient with BTK C481R mutation who had progressed on ibrutinib and venetoclax was then treated with pirtobrutinib and developed a BTK L528W mutation. NX-2127 treatment normalized blood counts, and suppressed both BTK C481R and L528W mutant clones coincident with >90% BTK and IKZF1 degradation in CD19+ B cells (Figure).
These findings uncover a heretofore unrecognized function of drug resistant BTK proteins, rendering BTK enzymatically dead yet retaining the ability to stimulate BCR signaling via scaffolding functions which bypass PLCγ2. Importantly, each of the recurrent BTK mutations encountered at clinical resistance to covalent and noncovalent BTK inhibitors are susceptible to the newly discovered clinical-grade BTK degrader compound described here, which is currently being tested in Phase 1b dose expansion in CLL with or without BTK mutations.
Disclosures
Thompson:Massachusetts Medical Society: Honoraria; Intellisphere, LLC: Honoraria; VJHemOnc: Honoraria; Curio Science: Honoraria; Brazilian Association of Hematology and Hemotherapy: Honoraria; MJH Life Sciences: Honoraria. Noviski:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Tan:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Brathaban:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Ye:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Cabuhat:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Yung:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Luliano:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Powers:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Robbins:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Rhodes:Genentech: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Velosbios: Research Funding; Morphosys: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; SeaGen: Consultancy; Abbive: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Verastem: Consultancy; Oncternal: Research Funding; Loxo Oncology: Research Funding; Epizyme: Research Funding. Zelenetz:AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics/Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Beigene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead/Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Juno Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; MBS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Roeker:Qilu Puget Sound Biotherapeutics: Research Funding; Ascentage: Consultancy; Aptose Biosciences: Research Funding; Abbott Laboratories: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Loxo Oncology: Consultancy, Other: Travel support, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Divested equity in a private or publicly-traded company in the past 24 months. Lu:Nurix Therapeutics, Inc.: Current Employment. Mato:AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; LOXO: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics, LLC: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Medscape: Honoraria; Octopharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Honoraria; Pfizer: Research Funding; Curio: Honoraria; Dava: Honoraria; BeiGene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics, Inc: Honoraria, Research Funding; Johnson & Johnson: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genmab: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; DTRM Biopharma: Honoraria, Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria; Nurix: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; PER: Honoraria; PerView: Honoraria. Abdel-Wahab:H3B Biomedicine, Foundation Medicine Inc, Merck, Prelude Therapeutics, and Janssen: Consultancy; H3B Biomedicine, LOXO Oncology, and Nurix Therapeutics: Research Funding; Envisagenics Inc., AIChemy, Harmonic Discovery Inc., and Pfizer Boulder: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Taylor:Karyopharm, Inc: Honoraria.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal